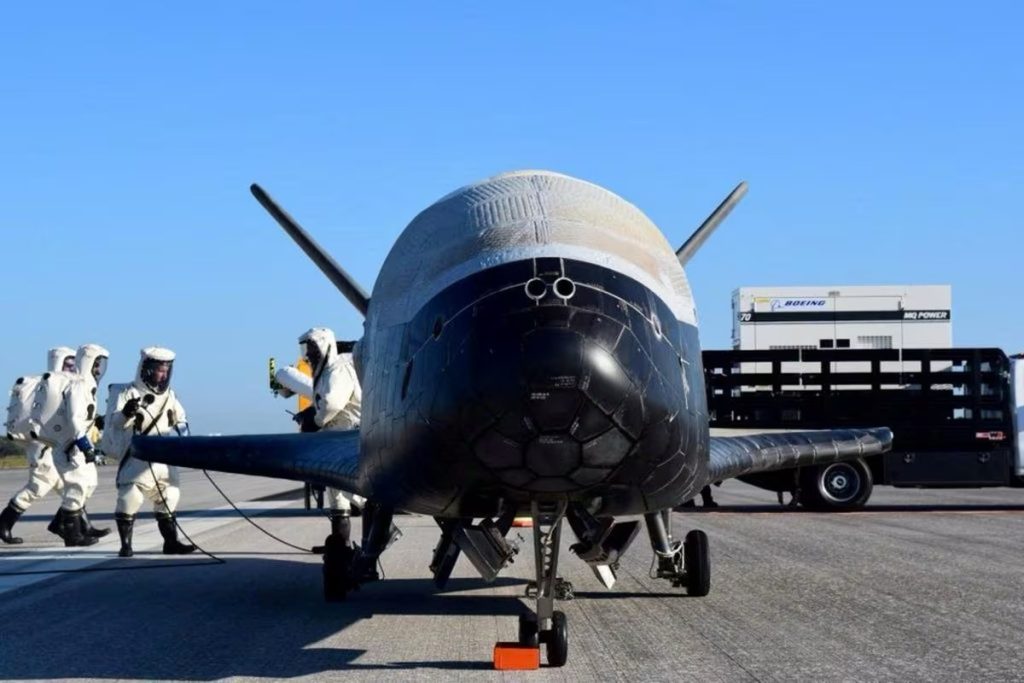

On Dec 28, at Cape Canaveral, Florida, after several delays and false starts, Elon Musk‘s SpaceX attempted to launch the X-37B spaceplane, a secretive military robot, on its seventh mission using a powerful rocket capable of reaching higher altitudes than in previous missions.
The SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket is scheduled to launch from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, during a 10-minute window starting at 8:07 p.m. EST (0107 GMT Friday), with a nighttime blast-off set to take place.
SpaceX encountered three aborted launch countdowns earlier this month due to inclement weather conditions and unspecified technical issues. The spacecraft was returned to its hangar before attempting the latest launch.
The latest development comes two weeks after China launched its reusable robot spaceplane, the Shenlong or “Divine Dragon,” on its third orbital mission since 2020, adding a new dimension to the escalating space race competition between the United States and China.
According to the most recent weather forecast, there is an 80% probability that Thursday’s flight will experience favorable launch conditions. The X-37B mission, carried out by the U.S. Space Force under the military’s National Security Space Launch initiative, remains shrouded in secrecy, with the Defense Department revealing minimal information.
The vehicle, built by Boeing and resembling a miniature space shuttle, is designed to carry various payloads and perform technology experiments during long-duration orbital flights. Once its mission is complete, it will return through the atmosphere and land on a runway, mimicking the landing of an airplane.
The spacecraft has flown six prior missions since 2010, with the first five launched aboard United Launch Alliance’s (a joint venture between Boeing and Lockheed Martin) Atlas V rockets and the most recent one launched in May 2020 using Elon Musk’s SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
The upcoming mission will be the first to use SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket, which can transport heavier payloads like the X-37B deeper into space and potentially reach geosynchronous orbit, located over 22,000 miles (35,000 km) above Earth’s surface.
Until now, the X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle has operated within low-Earth orbit, restricted to altitudes under 1,200 miles (2,000 km).
Exploring Novel Orbital Regimes and Seeds
The Pentagon remains tight-lipped about the spaceplane’s altitude on this mission. However, in a statement last month, the US Air Force Rapid Capabilities Office hinted that mission No. 7 would focus on testing innovative space domain awareness technologies and exploring new orbital regimes.




















+ There are no comments
Add yours